Crypto Market Cycles: Analyzing Historical Patterns for Future Predictions
December 5, 2025

by Coinmetro Editorial Team
December 5, 2025
Cryptocurrency markets, like traditional markets, move in cycles. These cycles typically include periods of growth, followed by corrections and consolidation. These changes can happen quickly in the crypto world, often influenced by market sentiment, regulations, and technological advancements. Understanding these market cycles is crucial for predicting future trends. By analyzing historical data, traders can make more informed decisions, reduce risk, and take advantage of opportunities.
Since Bitcoin's inception in 2009, the crypto market has experienced four major cycles. Currently, after a new all-time high followed by consolidation through most of 2024, we are now entering what many traders believe to be a new, vigorous bull run. What do you think crypto’s next move will be? Read this blog to understand the crypto market's cyclical phases and how to take advantage. You will learn about:
- What are crypto market cycles?
- Historical overview of major crypto market cycles
- Factors influencing cycles
- Using historical data to predict future market cycles
Lessons for the Next Crypto Surge - Analyzing Historical Bull Runs
Crypto market cycles are phases that repeat over time, driven by investor sentiment, market conditions, and external factors like regulation or technological advances. These cycles help explain the price fluctuations that are typical in cryptocurrencies.
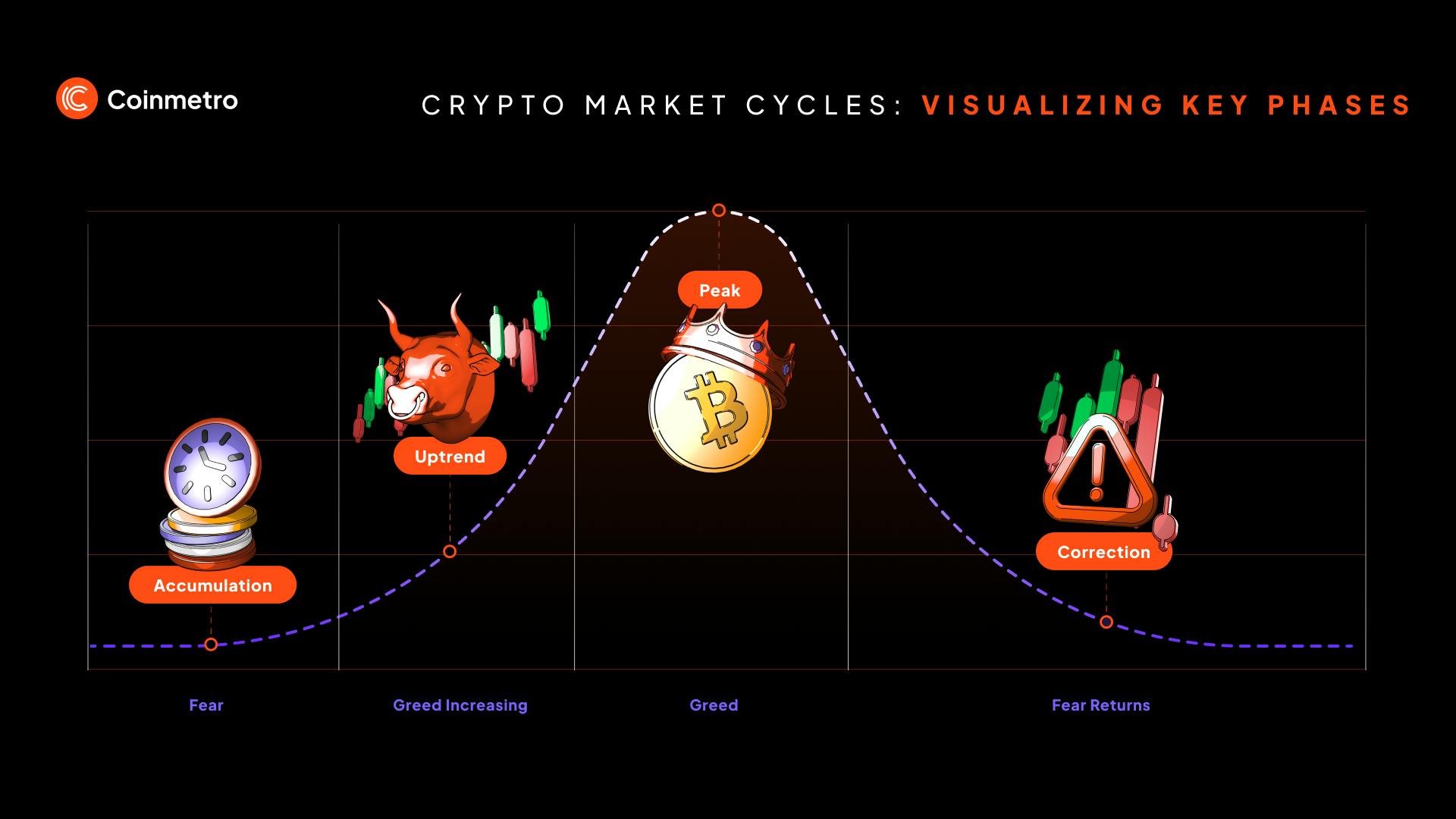
Each cycle has four key stages:
Accumulation phase: This is the beginning of the cycle, where prices are low, and investors start to re-enter the market after a downturn. During this phase, the market consolidates, and there is little media attention. It's characterized by cautious optimism among investors who are accumulating assets at low prices.
Uptrend/expansion phase: In this phase, prices rise as more people become interested in the market. Increased media coverage and growing optimism drive new investors into the market. Prices increase rapidly, creating momentum and leading to higher trading volumes.
Peak/bubble phase: This stage sees extreme optimism and high levels of speculation. Prices reach unsustainable levels due to investor euphoria. Media coverage is overwhelmingly positive, and new investors flood the market in fear of missing out (FOMO), leading to asset overvaluation.
Correction/bear phase: After the market peaks, prices fall as the bubble bursts. This correction can result in significant price declines of 60-80% from the all-time high. Panic selling often occurs during this phase, and the market eventually begins the cycle all over again.
Get Knowledgeable: The Twists and Turns of Crypto Volatility Explained
The cryptocurrency market has experienced several dramatic cycles, each shaping its future. By examining key historical events, we can better understand how market sentiment, external factors, and innovations drive these cycles.
In 2013, Bitcoin experienced its first major price surge, reaching over $1,000 for the first time. This rapid rise was driven by growing interest from early adopters, tech enthusiasts, and speculative investors. Increased media coverage and Bitcoin's potential as a new decentralized currency fueled the excitement.
However, the bubble burst shortly after, leading to a significant price crash. By early 2014, Bitcoin had lost over 80% of its value. The crash was triggered by multiple factors, including the Mt. Gox exchange hack, which undermined trust in the market. Additionally, regulatory scrutiny and security concerns further dampened market enthusiasm.
The 2017 bull run was primarily driven by the explosive growth of Initial Coin Offerings (ICOs). ICOs allowed startups to raise funds by issuing new cryptocurrencies. This innovation sparked a frenzy, as investors saw opportunities to make significant profits by getting in early on new projects.
Bitcoin's price skyrocketed to nearly $20,000 by December 2017, and other cryptocurrencies like Ethereum also surged. The bull market was marked by extreme optimism and massive inflows of capital.
However, this cycle ended with a dramatic crash in early 2018. Regulatory crackdowns on ICOs, particularly in the United States and China, contributed to the market downturn. Many ICO projects failed, resulting in substantial losses for investors. By the end of 2018, most cryptocurrencies had lost more than 80% of their value from their peaks.
The 2021 bull market was driven by several factors, including institutional adoption of Bitcoin, the rise of Decentralized Finance (DeFi), and mainstream media attention. Companies like Tesla and MicroStrategy added Bitcoin to their balance sheets, legitimizing crypto as an asset class.
Bitcoin reached an all-time high of $69,000 in November 2021. At the same time, the DeFi sector saw explosive growth, with projects like Uniswap, Aave, and Compound gaining traction. These platforms allowed users to borrow, lend, and trade cryptocurrencies without traditional intermediaries.
However, the market correction in 2022 brought significant losses. Concerns about inflation, rising interest rates, and global economic uncertainty led to a sell-off across the crypto market. By mid-2022, Bitcoin had already dropped by more than 50% from its peak, marking the end of the bull run. The collapse of FTX in November 2022 further deepened the crisis, pushing Bitcoin to its bear market bottom of around $15k. However, amid the tension, many investors seized the opportunity and accumulated Bitcoin and other altcoins at a major discount. Four months later, BTC was already trading at double the value.
Go Beyond the Fear and Greed Index: Crypto Market Sentiment Indicators
Investor emotions play a significant role in crypto cycles. The Fear and Greed Index is a popular tool for measuring market sentiment. When greed dominates, investors buy more, driving prices up. When fear sets in, panic selling occurs, leading to price drops. Market cycles often reflect extreme swings between these emotions.
Government actions and regulatory news heavily influence market cycles. For example, China’s ban on crypto mining in 2021 triggered a market sell-off. Conversely, supportive regulatory news can drive optimism and push prices higher, as seen with the approval of Bitcoin ETFs in certain countries.
New technological developments, such as blockchain upgrades or the launch of innovative projects, can fuel market growth. For example, Ethereum’s upgrade to Ethereum 2.0 improved scalability and security, which increased investor confidence and sparked a surge in the price of ETH.
As institutional investors like hedge funds and large corporations enter the crypto market, their involvement creates greater stability and liquidity. The introduction of Bitcoin ETFs and the decision by companies like Tesla to hold Bitcoin on their balance sheets pushed prices upward and added legitimacy to the market.
What You Need to Know About the Bitcoin and Crypto Market Cycles
Analyzing historical data is a powerful tool for predicting future crypto market cycles. Traders and investors rely on on-chain metrics, technical indicators, and sentiment analysis to anticipate price movements and market trends. These tools provide insights that help identify where we are in a market cycle and what might happen next.
On-chain metrics give traders a clear view of activity on blockchain networks, offering insights into supply, demand, and network health. Three key metrics are often used to predict market cycles:
Bitcoin halving events: Halving occurs roughly every four years, reducing the reward miners receive for adding new blocks to the Bitcoin blockchain. Historically, these events have triggered bull markets as the supply of new Bitcoin decreases, pushing prices higher.
Hash rates: The hash rate measures the computational power of a blockchain network. Higher hash rates indicate a secure and healthy network. A rising hash rate, especially on Bitcoin, often signals investor confidence, which can drive demand and price growth.
Trading volume: Trading volume shows how much of a cryptocurrency is being bought or sold. High volumes during an uptrend suggest strong market interest, while declining volumes during a downtrend may indicate weakening demand and a possible price drop.
Technical analysis tools help traders predict price trends, market momentum, and historical patterns. Some of the most popular indicators include:
RSI (Relative Strength Index): RSI helps traders spot overbought or oversold conditions. An RSI above 70 indicates that an asset is overbought and may be due for a correction. An RSI below 30 signals an oversold market, potentially signaling a buying opportunity.
Moving averages: Moving averages smooth out price data to help identify trends over a period. The 50-day and 200-day moving averages are often used to spot market shifts. When the 50-day average crosses above the 200-day average (a golden cross), it may indicate the start of a bull market. A death cross, where the 50-day falls below the 200-day, suggests a possible bear market.
MACD (Moving Average Convergence Divergence): MACD helps traders identify changes in momentum by comparing short-term and long-term moving averages. When the MACD line crosses above the signal line, it’s a potential buy signal, and when it crosses below, it may signal a sell.
Market sentiment can drive short-term price movements, making sentiment analysis an important tool. Traders can predict price swings by tracking social media trends, news coverage, and overall market mood.
Social media trends: Platforms like X (Twitter) and Reddit often reflect real-time market sentiment. Sudden spikes in discussions about a specific cryptocurrency can increase prices, while negative sentiment can trigger sell-offs.
News sentiment: Positive or negative news about regulations, technological developments, or institutional involvement can influence market sentiment. For instance, news of a major company adopting Bitcoin may push prices higher, while reports of regulatory crackdowns can lead to panic selling.
By studying past cycles, traders can spot patterns that may signal the start of new phases. Some key lessons include:
Bull markets follow halvings: Bitcoin halving events have historically led to bull runs, mainly because after halvings, the amount of new BTC entering the market is cut in half, contributing to Bitcoin's deflationary character. The most recent halving occurred in April 2024, followed by a consolidation period. Popular opinion predicts a price surge, driven by a growing supply crunch of BTC on exchanges.
Fear and greed drive market extremes: Market cycles are often driven by extremes in sentiment. When greed dominates, markets become overvalued, leading to a bubble. When fear takes over, prices crash, and opportunities arise for savvy investors to buy at low prices.
Institutional involvement stabilizes markets: As more institutional players enter the market, cycles may become less extreme. Institutional investments often bring stability and reduce volatility, making future cycles more predictable.
By analyzing historical patterns, traders can anticipate potential market shifts, whether during an uptrend or a correction. These insights allow for better risk management and more strategic market entries and exits.
Looking at past cycles helps you recognize the signs of market turning points, enabling you to act ahead of the curve. As the crypto market continues to evolve, with new technologies and regulations shaping the landscape, historical data will remain valuable in predicting future trends.
With the next bull cycle on the horizon, staying informed and applying lessons from the past will put traders in a stronger position to navigate the uncertainty and seize opportunities.
▶️ Watch: Bitcoin Market Cycle Theory
Join the Coinmetro community on Discord and Telegram, where forward-thinking traders and investors gather to share insights, explore new opportunities, and dive deep into cryptocurrencies. Should you need any help, please contact our world-class Customer Support Team via 24/7 live chat or email at hello@coinmetro.com.
To become a Coinmetro user today, Sign Up now or head to our new Exchange if you are already registered to experience our premium trading platform.
Tags
Related Articles

Regulatory Sandboxes: Fostering Crypto Innovation Within Legal Frameworks
The cryptocurrency industry’s fast rise fuels an important debate. Innovation aims to transform finance, enhancing speed and access. Yet, regulators…
5m

Crypto Options Trading: Strategies and Market Insights
Cryptocurrency markets have rapidly expanded beyond simple buying and selling. One of the most significant developments has been the rise of…
6m

The Rise of Social-Fi: Blending Social Media with Decentralized Finance
In recent years, social media and finance have started to merge, creating Social-Fi. This concept blends the engagement of social platforms with…
6m

DeFi Insurance Platforms to Watch in 2024
Decentralized Finance (DeFi) insurance addresses the growing need for insurance against hacks, smart contract failures, and other DeFi-related risks.…
7m