Understanding Web 3.0: A Deep Dive into the Decentralized Internet
December 5, 2025

by Kamil S
December 5, 2025
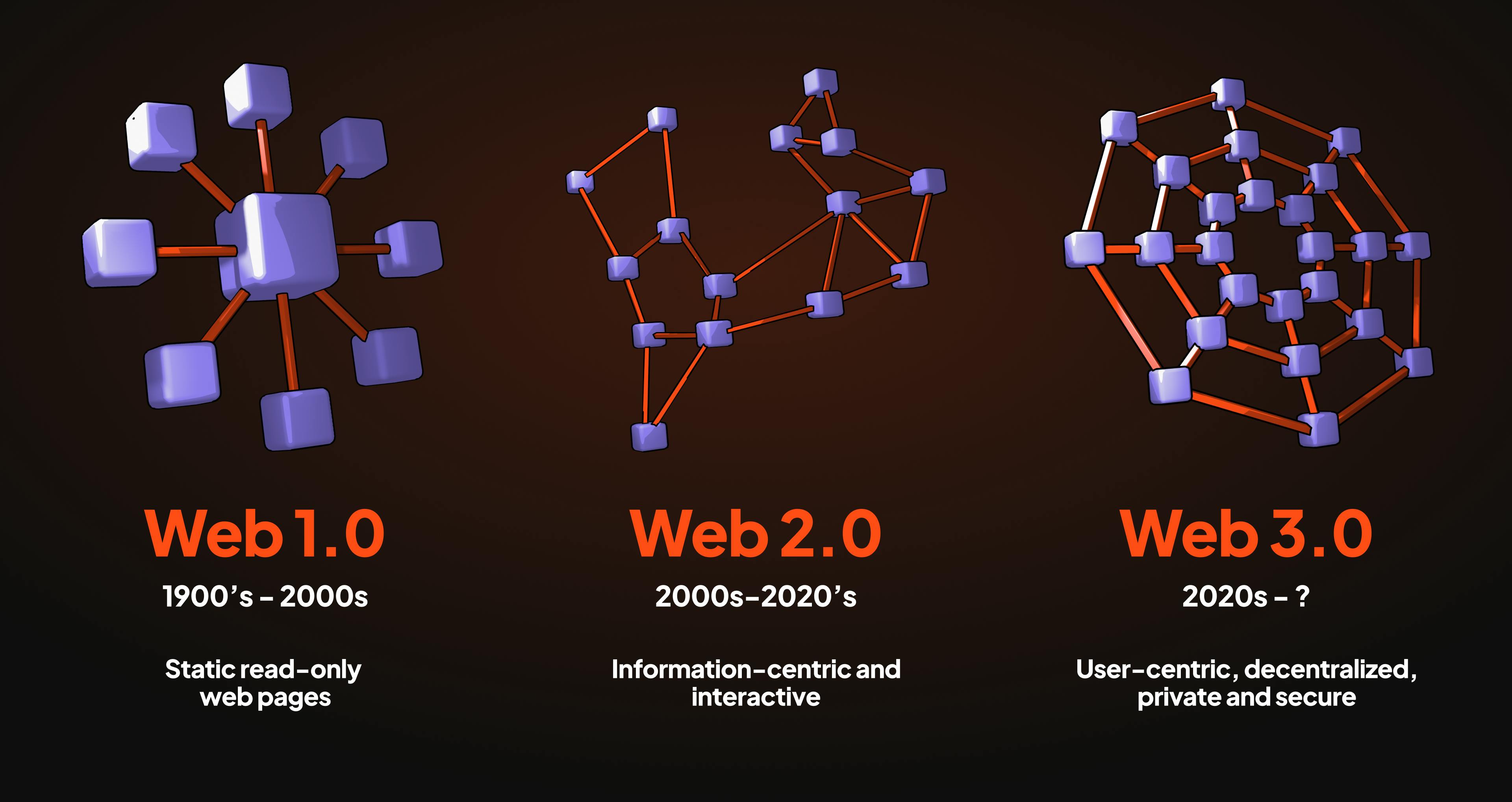
Web 3.0, also known as the decentralized internet, is an emerging technological paradigm that aims to revolutionize the way we interact with the online world and beyond. Unlike its predecessors, Web 1.0 and Web 2.0, which focused on centralized control, read-only - and later on - user-generated content, Web 3.0 embraces decentralization, direct peer-to-peer networks, and user-owned, user-monetized content. This is made possible by blockchain technology, essentially a distributed cryptographic network running immutable software code.
At its core, Web 3.0 seeks to empower users by giving them greater control over their data, privacy, and digital identities. It envisions a more transparent and secure online ecosystem where individuals can directly interact and transact with one another, eliminating the need for intermediaries. This shift towards decentralization opens up a myriad of possibilities, from decentralized finance (DeFi) and peer-to-peer marketplaces to decentralized social networks and autonomous organizations (DAOs).
With Web 3.0, the internet becomes a truly user-centric environment, where data ownership and digital sovereignty are paramount. It enables individuals to reclaim their digital rights and participate in a more equitable and democratic online space. As the decentralized internet continues to evolve, it holds the potential to reshape industries, empower individuals, and foster innovation in unprecedented ways.
In the 90s, Web 1.0 introduced static web pages, providing limited user engagement. With the arrival of Web 2.0, dynamic content and social media flourished, transforming the way we connect and share user-generated information. Now, Web 3.0 is revolutionizing the internet once again. Embracing decentralization, blockchain technology, and peer-to-peer networks, it offers users unprecedented control over their data, heightened privacy, and direct, trustworthy interactions. In Web 3.0, users not only create their own content, they also own it and can monetize it to their advantage.
Web 3.0 represents a shift towards a more inclusive, secure, and user-empowered internet. By embracing its principles, we can reshape online interactions, protect privacy, and unlock new possibilities for economic growth and technological advancement. Web 3.0, the next evolution of the internet, holds significant importance in shaping our digital future. Here's why it matters:
Decentralization: Web 3.0 introduces decentralization, reducing reliance on centralized authorities and enabling a more democratic and transparent online ecosystem. It empowers individuals by giving them control over their data and fostering a sense of ownership. You believe you own your email account hosted by a third party and your social media profiles? You don’t. Those are the property of the respective companies providing the service.
Enhanced Privacy: With Web 3.0, privacy takes center stage. By using cryptographic techniques and secure protocols, personal information is better protected from unauthorized access, ensuring user confidentiality.
Trust and Security: Web 3.0 leverages blockchain technology and smart contracts to establish trust and enhance security. By eliminating intermediaries and enabling direct peer-to-peer interactions, it reduces the risk of fraud, censorship, and data breaches.
Economic Opportunities: In Web 3.0, users have the potential to monetize their contributions and digital assets. It opens up new avenues for creators, entrepreneurs, and developers to participate in decentralized economies and benefit directly from their work.
Innovation and Collaboration: Web 3.0 fosters innovation by enabling the creation of decentralized applications (dApps) and interoperable platforms. It encourages collaboration and enables developers to build upon existing protocols, fostering a dynamic ecosystem of emerging solutions.
Web 3.0 encompasses a range of transformative features that shape the future of the internet. Some key characteristics include:
Semantic Web: Web 3.0, also known as the Semantic Web, focuses on machine-readable data and meaningful connections. It employs metadata, ontologies, and taxonomies to enable intelligent systems to understand and interpret information accurately.
Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning: Web 3.0 embraces the power of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) algorithms. These technologies enhance data analysis, automate processes, and enable intelligent decision-making to provide personalized and adaptive user experiences or business and industrial operations.
Ubiquitous Connectivity: With the proliferation of smart devices and IoT (Internet of Things) technologies, there is a growing expectation for constant connectivity and real-time access to information. Web 3.0 aims to fulfill these expectations by enabling pervasive connectivity across diverse devices and platforms.
Interoperability and Open-Source: With its interoperability and open-source principles, Web 3.0 encourages collaboration, innovation, and the democratization of technology.
By fostering interoperability, Web 3.0 promotes an environment where different blockchain networks, dApps, and platforms can seamlessly interact and share data. This breaks down silos and enables the development of integrated solutions that leverage the strengths of multiple systems. It encourages collaboration among developers, businesses, and users, leading to the creation of novel applications and services.
These key characteristics of Web 3.0 collectively redefine the internet landscape, providing more intelligent, connected, and user-centric experiences. By combining semantic technologies, seamless connectivity, new monetization opportunities, and open collaboration, Web 3.0 ushers in a new era of innovation and possibilities across the industries.
Blockchain technology is spearheading a transformative shift towards decentralization, cryptocurrency adoption, and the long awaited automation of trust:
Blockchain achieves decentralization in Web 3.0 through its consensus mechanisms, cryptographic algorithms, and peer-to-peer networks. By utilizing these components, blockchain enables an immutable and transparent environment where data integrity is assured, and transactions can occur directly between participants without intermediaries. The transparency and immutability of blockchain ensure a tamper-proof system that upholds the principles of decentralization. As opposed to Web 2.0 (the classic internet), which relies heavily on centralized servers and authorities for data storage and validation, Web 3.0 powered by blockchain technology distributes data across a network of nodes, removing single points of failure and enhancing the resilience and security of the system.
Enabled by blockchain technology, cryptocurrencies provide an alternative to traditional financial systems by offering decentralized digital assets. Furthermore, cryptocurrencies enable secure, borderless transactions, empower individuals with financial sovereignty, and foster inclusivity by enabling participation in global digital economies.
Instrumental to Web 3.0's automation revolution are smart contracts. These self-executing contracts, powered by blockchain technology, automate and streamline various processes across industries. Smart contracts eliminate the need for intermediaries, ensuring the integrity and transparency of agreements while enabling secure, efficient, and reliable transactions.
Decentralization is a paradigm that redistributes power and authority from a central entity to multiple participants. It offers a range of advantages while presenting some unique challenges.
Decentralized systems promote transparency, autonomy, and trust, fostering a more inclusive and equitable approach. They empower individuals and communities by giving them greater influence and control over their respective domains.
With decentralization, individuals enjoy greater data privacy and ownership, as their information is not controlled by a single entity, but rather cryptographically stored on-chain. Decentralized systems enhance security by distributing data across many nodes (computers in the network), reducing vulnerabilities to hacking and censorship. They also foster innovation and collaboration, as diverse participants can contribute and shape the ecosystem.
However, decentralization is not without challenges. Coordinating multiple participants in decentralized systems can be complex, requiring robust governance models and consensus mechanisms. Scalability issues may arise as networks grow in size and activity.
Regulatory frameworks may also pose challenges for decentralized systems. While Web 3.0 brings autonomy and transparency, it can create difficulties in ensuring compliance with existing regulations. Adapting regulatory frameworks to accommodate decentralized technologies is a complex task that requires collaboration between policymakers, industry experts, and stakeholders.
Despite the challenges, decentralization promotes a more democratic, transparent, and resilient approach to various domains, from technology to governance. By embracing decentralization, we can create systems that empower individuals, drive innovation, and foster trust. It is an ongoing journey of navigating complexity, making trade-offs, and continually refining decentralized approaches.
Ultimately, decentralization has the potential to reshape power dynamics and create a more inclusive and participatory future.
Decentralized applications (dApps) are transforming the digital landscape by leveraging blockchain technology to provide enhanced security, privacy, and user autonomy. Essentially, dApps are software applications that run on decentralized networks, allowing for transparent and tamper-proof operations. Unlike traditional applications, dApps are not controlled by a central authority, making them resistant to censorship. Instead, they rely on smart contracts - self-executing agreements stored on the blockchain - to govern their behavior.
Ethereum provides a robust infrastructure for dApp development through its support for smart contracts. Developers can leverage Ethereum's flexible platform to create and deploy dApps across various industries. The platform's wide adoption and vibrant ecosystem have contributed to its status as a leading choice for dApp development. Through Ethereum's decentralized network, dApps enable direct peer-to-peer interactions, eliminating the need for intermediaries. This approach enhances transparency, security, and trust among participants. Users of dApps can have greater control over their data, as information is stored securely on the blockchain and can only be accessed by authorized parties.
As the dApp landscape continues to evolve, Ethereum remains at the forefront, facilitating the creation of innovative and decentralized solutions. However, several other blockchain networks such as Polkadot, Avalanche, and Cardano, have also emerged as formidable contenders in the dApp space. The rise of these alternative networks demonstrates the increasing diversity and maturation of decentralized application platforms. Developers can now consider different blockchain networks based on their specific requirements, scalability needs, and user base.
In the Web 2.0 systems, centralized platforms collect vast amounts of user data, raising concerns about privacy breaches, data misuse, and surveillance. Moreover, providers of the service monetize user data through advertising and other avenues, which can be seen as a questionable practice.
On the other hand, users often have limited control over their personal information, relying on the trustworthiness of intermediaries. This centralized model poses risks to privacy and can lead to data manipulation or unauthorized use.
Web 3.0, built on the principles of decentralization, blockchain technology, and cryptographic protocols, empowers individuals with greater control over their data. By leveraging decentralized networks, Web 3.0 allows for peer-to-peer interactions, reducing the reliance on intermediaries and minimizing the collection and storage of personal information by central authorities. As a result, Web 3.0 enables individuals to reclaim their privacy and regain trust in the online ecosystem by shifting the balance of power from centralized entities to the users themselves.
Decentralized identity systems aim to give individuals ownership and control over their personal data, empowering them to choose how and when their information is shared. Through the use of cryptographic techniques, users can selectively disclose information while maintaining their privacy and anonymity.
However, the widespread adoption of Web 3.0 and decentralized identity systems requires education, technical advancements, and collaboration between stakeholders to ensure privacy best practices and standards are established.
Web 3.0 is poised to have a significant economic impact by reshaping the digital landscape and introducing novel opportunities for innovation and value creation. This new system, built on decentralized technologies like blockchain and cryptographic protocols, has the potential to revolutionize various aspects of the economy, from finance to supply chain management, to identification systems, healthcare and transportation.
One of the key drivers of Web 3.0's economic impact is the emergence of the token economy and decentralized finance (DeFi). Tokens, powered by blockchain technology, enable new forms of value exchange and ownership. They facilitate decentralized fundraising through initial coin offerings (ICOs) and enable innovative financial products and services through DeFi protocols, including lending, borrowing, and automated market-making.
Web 3.0 opens doors to new business models that challenge traditional centralized systems. Decentralized applications (dApps) allow for peer-to-peer interactions, enabling users to directly engage in commerce, content creation, and service provision. Tokenization of assets introduces fractional ownership and new revenue-sharing models, empowering creators and incentivizing user participation.
Web 3.0 has the potential to disrupt multiple industries. In finance, it can democratize access to financial services, enable global remittances, and revolutionize asset management. Supply chain management can benefit from increased transparency and traceability, reducing fraud and improving efficiency. Healthcare can be transformed through secure patient data management and interoperability. Entertainment and gaming industries can leverage non-fungible tokens (NFTs) for unique digital assets and enhanced fan engagement.
Furthermore, sectors such as real estate, energy, logistics, and governance are poised for transformation, leveraging the efficiency, security, and automation provided by Web 3.0 technologies. The economic impact of Web 3.0 extends beyond specific industries, fostering innovation, driving entrepreneurial opportunities, and reshaping the digital economy as a whole.
The future of Web 3.0 holds immense potential for transforming the digital landscape and shaping the way we interact with the internet. As we embark on this journey, it is important to consider the path and the challenges that lie ahead.
The path ahead for Web 3.0 involves further development and refinement of decentralized technologies, widespread adoption of blockchain-based solutions, and the emergence of innovative decentralized applications (dApps). We can expect increased interoperability between different blockchain networks, improved scalability, and enhanced user experiences as the ecosystem evolves.
This may lead to a climate where users can easily monetize their digital assets and contributions.
Furthermore, finance is a field where Web 3.0 can potentially create the biggest value for users, offering everyone unprecedented access, control, and opportunities.
Additionally, governmental adoption of Web 3.0 technologies can streamline administrative processes, enhance transparency in public services, and promote citizen-centric governance.
While Web 3.0 offers numerous benefits, there are several barriers to its widespread adoption. These include scalability limitations, regulatory uncertainties, and the need for education and awareness. To overcome these barriers, concerted efforts from various stakeholders are required.
Scaling solutions like layer 2 protocols and sharding techniques should be developed for Web 3.0's scalability. Regulatory uncertainties need clear legal frameworks that efficiently leverage innovation and user protection. Educating individuals, businesses, and organizations on the benefits of Web 3.0 through programs and workshops is crucial for fostering its adoption and unlocking its full potential. Key industry collaborations may potentially address interoperability, data privacy, and user experience, driving adoption forward. Lastly, prioritizing user-centric design and integrating Web 3.0 seamlessly into existing systems will encourage mass adoption.
A fully decentralized internet, as envisioned in Web 3.0, would have profound consequences. It would empower individuals with greater control over their data, significantly reduce privacy concerns, limit the reliance on centralized intermediaries, and foster global collaboration. This has the potential to truly democratize access to information and services, promote financial inclusion, and enable new forms of peer-to-peer governance and decision-making.
However, a fully decentralized internet also raises some questions. The shift away from centralized authorities may introduce new challenges in terms of accountability, dispute resolution, and the potential for misuse or illegal activities. Striking the right balance between decentralization and necessary regulations will be essential to ensure a safe and sustainable digital ecosystem.
To prepare yourself or your business for Web 3.0, there are several key steps you can take to stay ahead of the curve and take advantage of emerging opportunities. Here are some strategies to consider:
Educate yourself: Familiarize yourself with the concepts and technologies associated with Web 3.0, such as blockchain, decentralized applications (dApps), smart contracts, and artificial intelligence. Stay updated with industry trends and developments.
Embrace decentralization: Web 3.0 is characterized by decentralization and increased user control. Explore how you can integrate decentralized systems and technologies into your business model. Consider using blockchain for transparency, security, and peer-to-peer transactions.
Enhance data privacy and security: As data ownership and privacy become increasingly important in Web 3.0, prioritize security measures to protect user data. Implement encryption, user consent mechanisms, and robust cybersecurity practices.
Foster interoperability: Web 3.0 aims to enable seamless communication and data exchange between different platforms and applications. Explore interoperability standards and protocols to ensure compatibility and collaboration with other businesses and networks.
Embrace the power of DeFi: Decentralized finance platforms and cryptocurrencies are gaining traction in Web 3.0. Discover how DeFi can enhance your financial operations with decentralized lending, borrowing, or tokenization. Furthermore, explore the potential of decentralized fundraising through initial coin offerings (ICOs) or token sales. DeFi allows you to access a global network of investors, empowering you to raise capital in a decentralized and inclusive manner.
By proactively embracing the principles and technologies of Web 3.0, you can position yourself and your business to leverage the opportunities and stay competitive in the decentralized digital future.
Join the Coinmetro community on Discord and Telegram, where forward-thinking traders and investors gather to share insights, explore new opportunities, and dive deep into the world of cryptocurrencies. Should you need any help, feel free to reach out to our world-class Customer Support Team via 24/7 live chat or email at hello@coinmetro.com.
To become a Coinmetro user today, Sign Up now, or head to our new Exchange if you are already registered and experience our premium trading platform.
Tags
Related Articles

Regulatory Sandboxes: Fostering Crypto Innovation Within Legal Frameworks
The cryptocurrency industry’s fast rise fuels an important debate. Innovation aims to transform finance, enhancing speed and access. Yet, regulators…
5m

Crypto Options Trading: Strategies and Market Insights
Cryptocurrency markets have rapidly expanded beyond simple buying and selling. One of the most significant developments has been the rise of…
6m

The Rise of Social-Fi: Blending Social Media with Decentralized Finance
In recent years, social media and finance have started to merge, creating Social-Fi. This concept blends the engagement of social platforms with…
6m

DeFi Insurance Platforms to Watch in 2024
Decentralized Finance (DeFi) insurance addresses the growing need for insurance against hacks, smart contract failures, and other DeFi-related risks.…
7m