The Future of Decentralized Bandwidth and Storage Solutions
December 5, 2025
by Coinmetro Editorial Team
December 5, 2025
The digital age boosts data creation, demanding secure, scalable data management solutions. Centralized systems for bandwidth and storage face big issues. Data breaches rise, costs climb, and power concentrates with tech giants, risking monopolies.
As demand for data management grows, centralized systems show clear limits. They struggle to scale, relying on weak points that hurt security and trust. Privacy worries increase when few control data and users lose power over it.
This article explores decentralized bandwidth and storage as fresh innovations. These systems spread data across many points (nodes), cutting risks tied to central servers. They promise better security, lower costs, and more user control.
We will explore how decentralized storage and bandwidth systems work and their benefits. We will cover real uses, future possibilities, and some tough spots they face. You’ll get a full look at this game-changing field.
In this blog, you will learn about:
- Decentralized bandwidth and storage
- Advantages of decentralized solutions
- Real-world applications and use cases
- Challenges
Learn More: 5 Storage Tokens Every Crypto Enthusiast Should Know
Decentralized bandwidth and storage refer to systems that spread data and network resources across many independent nodes. Unlike traditional setups, they don’t rely on centralized servers. This approach boosts security, improves resilience, and gives users more control. It also reduces risks like system failures and data breaches while enabling more efficient resource sharing.
As mentioned, decentralized networks store data across multiple nodes, not just one spot. These nodes—computers, servers, or devices—each hold a piece of the data securely. The system keeps data safe and available with backups and encryption.
Blockchain powers many of these networks with a clear, unchangeable record of changes. Peer-to-peer setups let nodes share data directly, skipping middlemen for efficiency. This design enhances security and strengthens the network by removing single points of control.
Several projects are leading the way in decentralized bandwidth and storage solutions:
Filecoin: An open-source cloud storage marketplace, protocol, and cryptocurrency that incentivizes users to rent out spare storage space. It allows users to store and retrieve data in a decentralized manner.
Storj (STORJ): A decentralized cloud storage network that encrypts and distributes data across a global network of nodes, providing high levels of security and redundancy.
Sia (SC): Sia offers decentralized cloud storage by splitting, encrypting, and distributing files across a global decentralized network. Compared to traditional cloud storage services, it aims to reduce costs and increase privacy.
Holo (HOT): Holochain enables decentralized application hosting on a peer-to-peer network, which is not limited to storage but also covers bandwidth and computing power. Holo offers a unique approach by facilitating a distributed cloud that users own and operate.
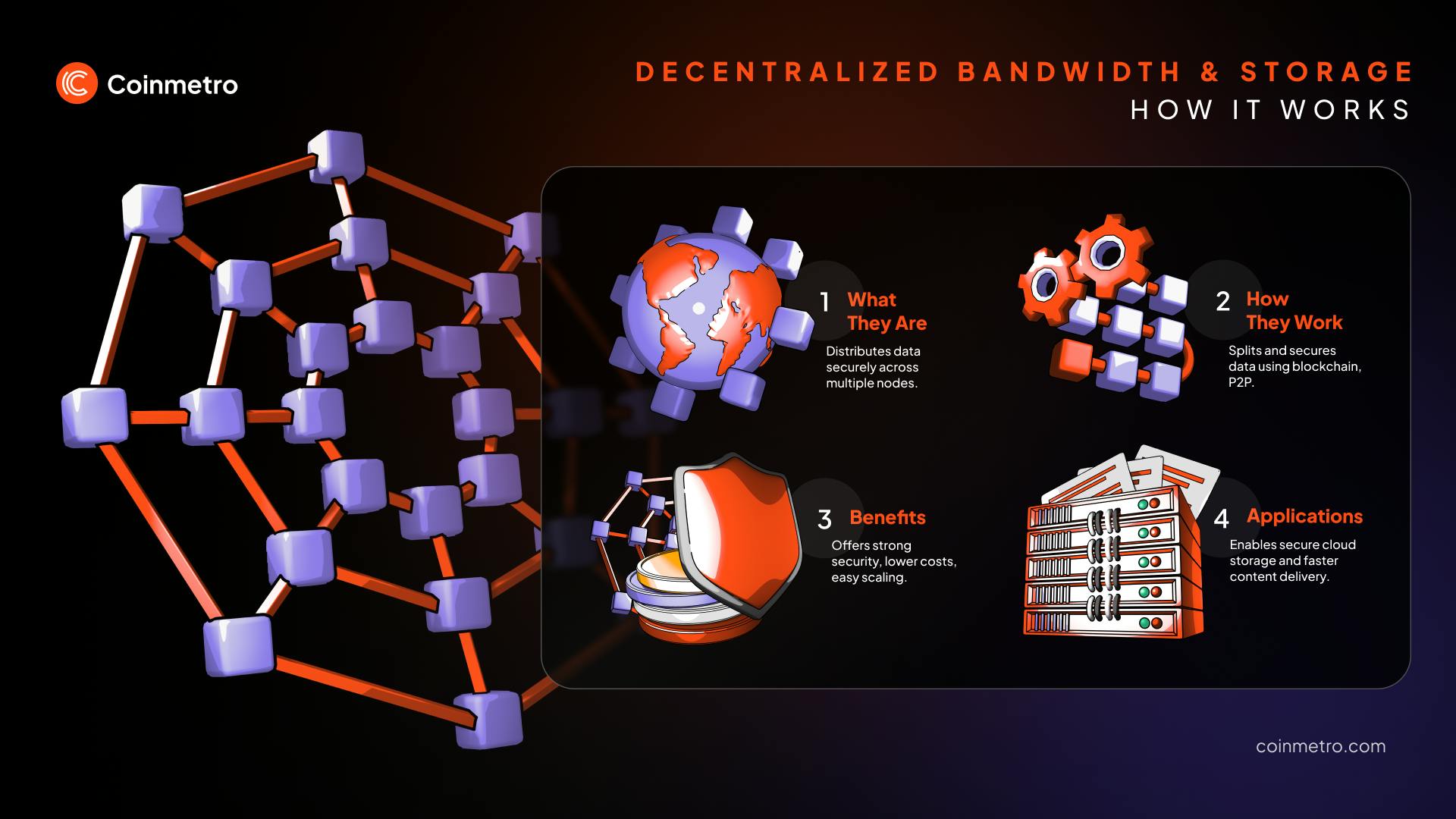
Decentralized solutions boost data security with encryption and distributed networks. They split data into pieces and store it across many nodes to prevent hacking. Even if one node gets hit, encryption and distribution keep the rest safe.
Decentralized systems cut costs by skipping middlemen and using spare resources. Centralized setups rely on pricey go-betweens for data management and storage. Peer-to-peer networks ditch those fees and tap unused storage, making things cheaper.
Decentralized solutions scale easily to handle growing data needs. Centralized systems falter, needing big cash for new gear to keep up. Adding nodes lets decentralized networks grow fast without huge upgrades anywhere.
Decentralized solutions give users full control over their own data. Centralized systems can hand data to third parties who might misuse it without permission. With decentralized systems, however, users pick how and where their data goes, boosting privacy and trust.
Get Familiar with Decentralized File Storage Solutions like IPFS & Filecoin
Decentralized bandwidth solutions can improve Content Delivery Networks. Traditional CDNs use centralized servers to send content, which costs more and scales poorly. Peer-to-peer networks share the load, cutting costs and boosting speed.
People and businesses pick decentralized cloud storage for security and savings. These platforms spread data across many nodes worldwide, keeping it safe with encryption. Tools like Storj and Sia let users rent spare space, slashing costs and boosting privacy.
Decentralized bandwidth lifts media and entertainment with better streaming and gaming. Centralized systems lag or buffer during busy times, but nodes can share the workload. Projects like Theta Network use user bandwidth to improve quality while paying them back in a win-win relationship.
Decentralized storage and bandwidth help companies handle big data without relying on centralized providers that could be vulnerable to attacks or downtime. These systems scale easily and stay strong against attacks or downtime. Finance and e-commerce can gain uptime and flexibility while keeping costs low.
Trade OctaSpace (OCTA) - The Platform Democratizing Internet Infrastructure
Decentralized storage networks face several key adoption issues. Many users lack awareness about how these systems work and their benefits over standard options. Setting up these networks requires technical skills that many potential users don't have. This creates a real barrier to wider use. Unclear regulations also cause problems for adoption. Companies often avoid these systems when legal status remains uncertain.
These networks face notable technical challenges as well. Data access tends to be slower because files are stored across many locations. This differs from central systems, where all data sits in one place. Ensuring constant data access is another major concern. When parts of the network go offline, users may lose access to their files. This risk makes many users stick with traditional systems.
Most governments lack clear rules for these new storage systems. This creates risk for businesses using the technology. Some regions might impose strict limits if they view these systems as threats. Without proper oversight, these networks might enable illegal activities. This legal gray area makes many companies hesitate to adopt the technology.
Different networks often struggle to work together effectively. Each system uses its own methods and security measures. The lack of shared standards prevents smooth data exchange between systems. Users find it hard to move content between different networks. They may not be able to combine features from various systems easily. This limitation may reduce the overall potential of the technology.
Comparison: The Economics of Centralized and Decentralized Cloud Storage
Decentralized storage and bandwidth solutions show great promise for changing data management. These systems offer better security, growth potential, and lower costs for both companies and people. More users are turning to these options to gain control over their data. They want more privacy and protection against the risks of central systems.
However, these systems face several key challenges that need solutions. Rules for these networks remain unclear in many places. The technical setup can be complex for new users. Different systems often struggle to work together properly. New standard methods and clearer rules will help solve these problems.
Decentralized bandwidth and storage systems mark a major change in how we store and access data globally. As these systems improve, they will become vital to digital networks. Success will hinge on embracing new ideas and effectively putting them into action. Those who adopt these systems early will potentially see the biggest benefits from this shift.
What decentralized storage and bandwidth project tokens are you holding in your portfolio?
Buy Storj (STORJ), Holo (HOT), and 80+ other cryptocurrencies on the Coinmetro exchange and learn more about specific decentralized storage projects in this article.
▶️ Watch: Decentralized Storage - A $778 Billion Opportunity?
Join the Coinmetro community on Discord and Telegram, where forward-thinking traders and investors gather to share insights, explore new opportunities, and dive deep into cryptocurrencies. Should you need any help, please contact our world-class Customer Support Team via 24/7 live chat or email at hello@coinmetro.com.
To become a Coinmetro user today, Sign Up now or head to our new Exchange if you are already registered to experience our premium trading platform.
Tags
Related Articles

Regulatory Sandboxes: Fostering Crypto Innovation Within Legal Frameworks
The cryptocurrency industry’s fast rise fuels an important debate. Innovation aims to transform finance, enhancing speed and access. Yet, regulators…
5m

Crypto Options Trading: Strategies and Market Insights
Cryptocurrency markets have rapidly expanded beyond simple buying and selling. One of the most significant developments has been the rise of…
6m

The Rise of Social-Fi: Blending Social Media with Decentralized Finance
In recent years, social media and finance have started to merge, creating Social-Fi. This concept blends the engagement of social platforms with…
6m

DeFi Insurance Platforms to Watch in 2024
Decentralized Finance (DeFi) insurance addresses the growing need for insurance against hacks, smart contract failures, and other DeFi-related risks.…
7m