DeFi Lending and Borrowing: A Beginner's Guide
December 5, 2025
by Coinmetro Editorial Team
December 5, 2025
DeFi (Decentralized Finance) uses blockchain technology to offer financial services without banks. Platforms like Ethereum, Solana, and Polygon rely on smart contracts for transactions. These contracts provide transparency, security, and access for users to lend, borrow, or trade.
DeFi cuts out central control, supporting financial access and innovation globally. Lenders earn better interest rates, while borrowers potentially get cheaper loans. This blog covers DeFi lending and borrowing, showing their benefits. You will learn about:
- What is DeFi lending and borrowing?
- How DeFi lending works
- How DeFi borrowing works
- Advantages of DeFi lending and borrowing
- Risks and challenges in DeFi lending and borrowing
- Successful DeFi lending and borrowing platforms
Discover Passive Income in Crypto: Staking, Lending, and Yield Farming
DeFi lending and borrowing provide decentralized financial services for users. People lend crypto to gain interest or borrow using collateral. Blockchain-based smart contracts manage transactions, ensuring clarity, low fees, and wide access.
Traditional finance uses banks to handle transactions and charge fees. DeFi relies on blockchain and smart contracts to automate financial products securely. This method lowers costs, speeds up processes, and helps unbanked groups.
Smart Contracts: Coded agreements that execute terms on their own. They process transactions without middlemen, reducing errors. Automation builds trust and efficiency in DeFi platforms.
Blockchain Technology: A shared ledger tracking transactions across a network. Each record stays secure, clear, and unchangeable, ensuring safety. DeFi systems use blockchain for reliable lending and borrowing.
Comparative Analysis: Decentralized Finance (DeFi) vs. Traditional Finance
Liquidity pools are essential to DeFi lending. Users deposit their cryptocurrency into these pools, creating a reserve of funds that borrowers can access. These pools operate via smart contracts, which automate and secure transactions. When lenders add their assets to the pool, they provide the liquidity needed for borrowing. This system ensures that funds are always available for borrowers while allowing lenders to earn interest on their deposits.
Choose a DeFi platform: Select a trusted DeFi platform like Aave, Compound, UniSwap, or MakerDAO.
Connect your wallet: Use a cryptocurrency wallet to connect to the platform.
Deposit assets: Transfer your crypto assets to the platform’s liquidity pool.
Approve the transaction: Confirm the transaction through your wallet to complete the deposit.
Earn interest: Once deposited, your assets start earning interest based on the demand and supply dynamics of the pool.
Lenders earn interest by providing liquidity to the pool. The interest rates are typically higher than traditional savings accounts, reflecting the demand for borrowed assets. The platform calculates interest in real time, and lenders can withdraw their assets along with the earned interest at any time. Additionally, some platforms offer reward tokens as an extra incentive for providing liquidity.
Discover Features and Comparison of the Best Crypto Lending Platforms
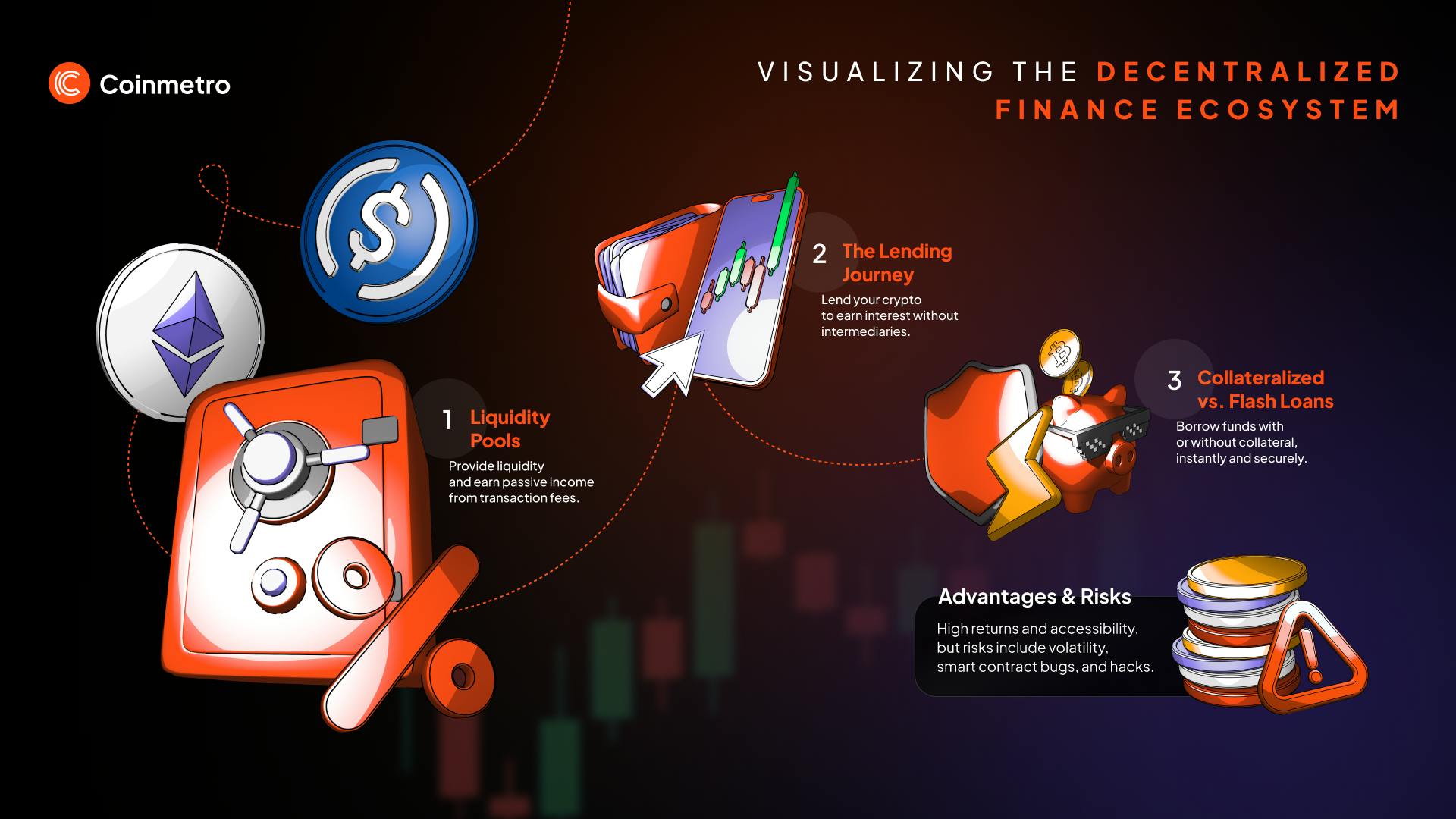
Collateralized Loans: In DeFi, collateralized loans require borrowers to provide cryptocurrency as collateral to secure a loan. The collateral's value must exceed the loan amount to mitigate risk. If the borrower fails to repay the loan, the lender can liquidate the collateral to recover the funds. Popular platforms offering collateralized loans include Aave, Compound, and MakerDAO.
Flash Loans: Flash loans are a unique DeFi feature that allows users to borrow funds without collateral, provided they repay the loan within the same transaction block. These loans are mainly used for arbitrage, refinancing, or exploiting price discrepancies across different platforms. Flash loans are available on platforms like Aave and dYdX.
Select a DeFi platform: Choose a reliable platform such as Aave, Compound, or MakerDAO.
Connect your wallet: Use a cryptocurrency wallet to connect to the chosen platform.
Choose loan type: Decide between a collateralized loan or a flash loan.
Deposit collateral: For collateralized loans, deposit the required collateral into the platform.
Specify loan amount: Enter the amount you wish to borrow.
Approve the transaction: Confirm the transaction through your wallet.
Receive funds: The platform transfers the borrowed funds to your wallet instantly.
Leverage Trading: Borrowers can use loans to increase their trading positions, potentially amplifying their gains.
Arbitrage Opportunities: Flash loans enable users to exploit price differences across exchanges without risking their own funds.
Liquidity Access: Borrowers can access liquidity without selling their assets, avoiding potential tax events.
Investment Opportunities: Users can borrow funds to invest in other DeFi projects or tokens, diversifying their portfolios.
Learn How Yield Farming Works
DeFi platforms allow anyone with internet access to lend or borrow. No bank account or credit history is required to participate. This setup supports underbanked regions, boosting financial inclusion globally.
DeFi cuts out intermediaries like banks, lowering transaction fees significantly. Lenders earn higher interest rates compared to traditional savings accounts. Rates adjust based on supply and demand, benefiting both lenders and borrowers.
DeFi transactions happen quickly through automated smart contracts on a blockchain. Unlike slow traditional banking, DeFi delivers near-instant results for users. Blockchain logs every transaction, ensuring clarity, trust, and real-time tracking.
DeFi lending and borrowing operate without credit checks. Borrowers provide cryptocurrency as collateral, which mitigates the need to assess creditworthiness. This system opens up borrowing opportunities for individuals who might not qualify for loans in traditional financial systems due to poor credit scores.
Smart contracts, the backbone of DeFi platforms, are susceptible to bugs and exploits. Even minor coding errors can lead to significant financial losses. For example, in 2020, a vulnerability in the smart contract code of the bZx protocol resulted in a nearly $1 million loss. Regular audits and code reviews are essential to mitigate these risks, but they haven't been eliminated entirely.
Cryptocurrencies are known for their price volatility. When prices fluctuate, the collateral value in DeFi loans can change rapidly, potentially leading to liquidation if the collateral value drops below the required threshold. Additionally, liquidity providers in DeFi pools may experience impermanent loss, which occurs when the value of the assets they deposited changes compared to holding the assets individually.
The regulatory environment for DeFi is still evolving. Governments around the world are assessing how to regulate these decentralized platforms. Regulation changes can impact DeFi operations, potentially leading to restrictions, increased compliance costs, or even shutdowns of certain services. For instance, the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) has indicated that some DeFi activities might fall under securities laws.
Due to the large sums of money involved, DeFi platforms are attractive targets for hackers. In 2021, Poly Network suffered a hack that stole over $600 million, although the funds were later returned. Such incidents highlight the importance of robust security measures and the ongoing risk of attacks.
Discover DeFi: The Ultimate Beginner's Guide to Decentralized Finance
MakerDAO is a decentralized lending platform that allows users to create DAI, a stablecoin pegged to the US dollar. Users lock up Ethereum and other cryptocurrencies as collateral in Maker Vaults to mint DAI. The platform's decentralized nature and robust governance system, managed by MKR token holders, ensure stability and transparency. MakerDAO has become a cornerstone of the DeFi ecosystem by providing a stable, decentralized currency.
UniSwap is primarily known as a decentralized exchange (DEX) but also offers lending and liquidity provision services. Users provide liquidity to UniSwap pools by depositing equal values of two tokens, earning a portion of the trading fees in return. UniSwap’s automated market maker (AMM) system allows for seamless and permissionless token swaps, making it a vital part of the DeFi infrastructure.
Compound is a popular DeFi lending platform allowing users to borrow various cryptocurrencies. Users deposit assets into liquidity pools and earn interest, while borrowers can take out loans against their crypto holdings as collateral. The platform's native COMP token provides governance rights, allowing users to participate in decision-making processes. Compound's automated and transparent interest rate model has made it a preferred choice for many DeFi participants.
Aave is a decentralized lending protocol that offers a wide range of cryptocurrencies for lending and borrowing. Known for its innovative features like flash loans and credit delegation, Aave allows users to borrow without collateral for brief periods or delegate their borrowing power to others. The platform’s interest rates are dynamically adjusted based on supply and demand, ensuring an efficient and competitive lending environment.
dYdX is a DeFi platform that provides a suite of financial tools, including margin trading, spot trading, and lending. It allows users to borrow and lend assets with varying leverage, offering advanced trading features that cater to experienced traders. The platform’s smart contracts ensure security and transparency, making it a robust option for those looking to engage in complex financial activities on the blockchain.
DeFi lending and borrowing use blockchain for financial services, providing an alternative to traditional banks. Platforms like Compound, Aave, and MakerDAO enable smart contract transactions. Users lend, borrow, or arbitrage with clarity and safety. DeFi platforms need only an internet connection to join. They offer financial access to users from all backgrounds, supporting underserved communities around the world.
DeFi Lending and Borrowing Basics: DeFi allows users to lend their crypto to earn interest or borrow against their crypto as collateral. This system operates without intermediaries, using smart contracts to manage transactions.
How DeFi Lending Works: Users deposit their crypto into liquidity pools, providing funds for borrowers. Lenders earn interest based on demand and supply dynamics.
How DeFi Borrowing Works: Borrowers can take out collateralized loans or flash loans. The process involves selecting a platform, connecting a wallet, depositing collateral, and receiving funds instantly.
Advantages: DeFi offers accessibility, lower costs, higher interest rates, speed, transparency, and no need for credit checks.
Risks: Potential risks include smart contract vulnerabilities, market volatility, regulatory uncertainties, and security threats.
By embracing the principles of decentralization, transparency, and inclusivity, DeFi lending and borrowing democratize financial services and pave the way for innovative financial ecosystems that challenge traditional banking paradigms.
Join the Coinmetro community on Discord and Telegram, where forward-thinking traders and investors gather to share insights, explore new opportunities, and dive deep into cryptocurrencies. Should you need any help, please contact our world-class Customer Support Team via 24/7 live chat or email at hello@coinmetro.com.
To become a Coinmetro user today, Sign Up now, or head to our new Exchange if you are already registered to experience our premium trading platform.
Tags
Related Articles

Regulatory Sandboxes: Fostering Crypto Innovation Within Legal Frameworks
The cryptocurrency industry’s fast rise fuels an important debate. Innovation aims to transform finance, enhancing speed and access. Yet, regulators…
5m

Crypto Options Trading: Strategies and Market Insights
Cryptocurrency markets have rapidly expanded beyond simple buying and selling. One of the most significant developments has been the rise of…
6m

The Rise of Social-Fi: Blending Social Media with Decentralized Finance
In recent years, social media and finance have started to merge, creating Social-Fi. This concept blends the engagement of social platforms with…
6m

DeFi Insurance Platforms to Watch in 2024
Decentralized Finance (DeFi) insurance addresses the growing need for insurance against hacks, smart contract failures, and other DeFi-related risks.…
7m