Gas Fees Explained: Why Ethereum Transactions Can Be Expensive
5 de diciembre de 2025
by Coinmetro Editorial Team
5 de diciembre de 2025
Ethereum has introduced the concept of "gas fees," a critical part of any transaction on the network. These fees represent extra costs that come with every transaction. They help keep the network running and safe by paying for the computing power needed.
Gas fees go to the network's validators, who check and record transactions. Each action on Ethereum has a cost, which helps prevent spam and misuse. Gas fees incentivize validators on Ethereum's Proof of Stake network to include transactions in the blockchain.
The cost of gas fees may change often. When the network is busy, fees usually increase. Complex transactions cost more than simple transfers. Users of DeFi apps and NFT markets feel this impact the most, as they make many transactions. Understanding how gas fees work and what drives their cost is essential for anyone using Ethereum. This knowledge helps users plan their actions on the network, from basic transfers to complex smart contract use. Understanding fee patterns can help users save money and time.
In this blog, you will learn about:
- What are gas fees?
- Why are gas fees needed?
- How are gas fees calculated?
- Factors affecting Ethereum gas prices
- Examples and current costs
- How users can reduce costs
- Alternatives to Ethereum
Read a Comprehensive Guide about Ethereum 2.0 Staking Rewards
Gas fees are small payments required to process transactions and execute smart contracts on the Ethereum network. These fees compensate validators for their computational resources, ensuring network security and functionality.
“Gas” represents the computational power needed to perform actions on the Ethereum network, whether sending ETH, executing smart contracts, or using decentralized applications (dApps). Each action on Ethereum requires a certain amount of gas, with more complex transactions needing more gas. Users pay gas fees in ETH, Ethereum’s native cryptocurrency, with the total cost based on the gas used and the gas price at that moment.
A user might need around 21,000 gas units for a basic ETH transfer. If the gas price is 50 gwei (one-billionth of one ETH), the total cost for the transaction would be 21,000 gas * 50 gwei, translating to 0.00105 ETH (depending on the current ETH price). Complex actions like interacting with DeFi protocols or NFT marketplaces might require more gas, leading to higher fees, especially during high network traffic.
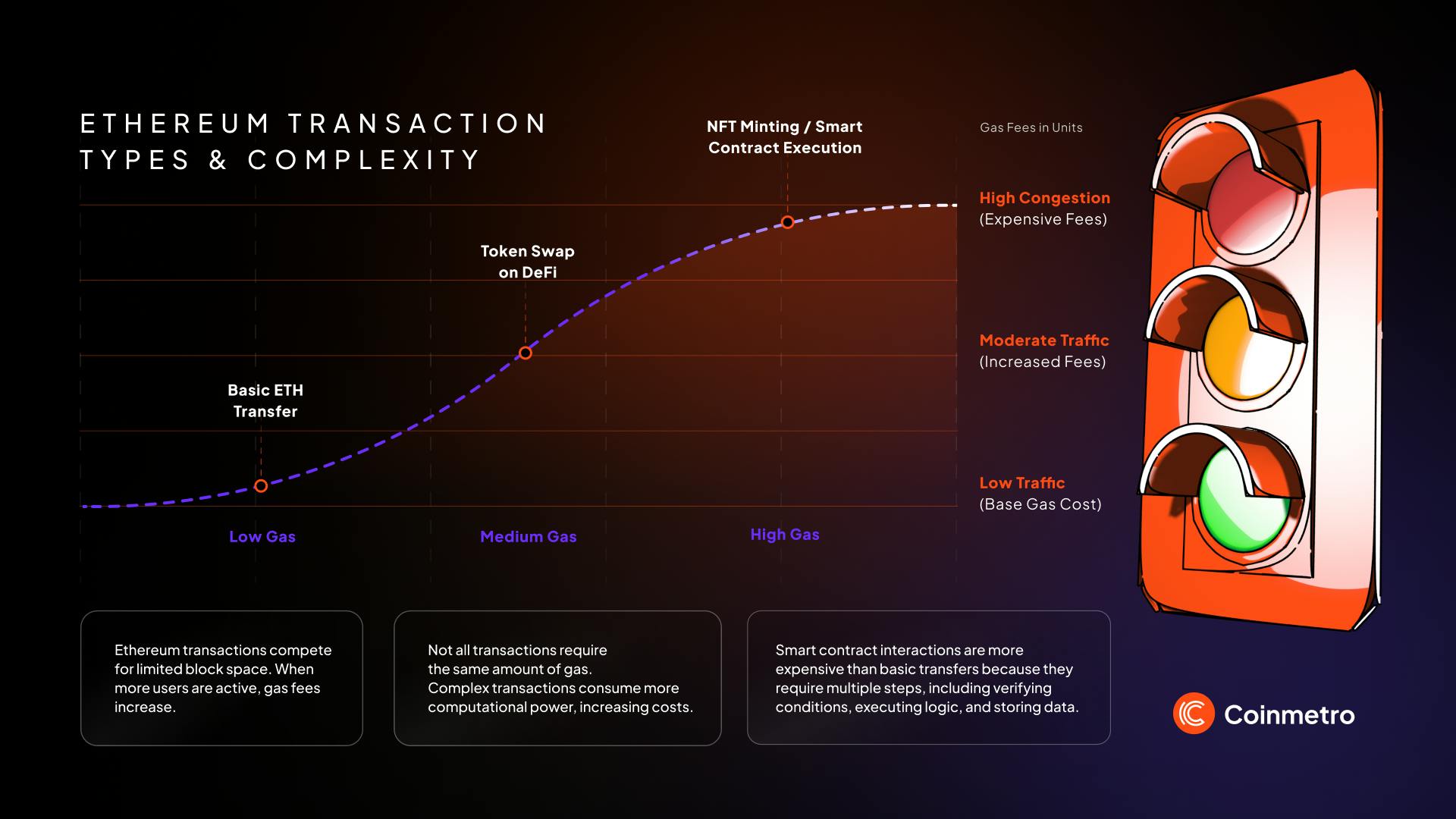
Network Support and Security: Gas fees are essential to Ethereum’s security. Every action on the network needs computing power to work. The network charges fees to stop spam and maintain network integrity. These fees directly support a secure and efficient network. They are used for covering processing and storing transaction data costs across decentralized nodes.
Compensation for Validators: Validators play a key role in validating and adding transactions to the blockchain. Gas fees reward validators for their efforts, paying for the equipment and power needed for this work. This reward system motivates validators to process transactions, ensuring the network runs smoothly.
Prioritizing Transactions: Gas fees help prioritize transactions during network congestion. Users can pay more to have their transactions processed more quickly. Higher fees move transactions to the front of the line. This system is helping the network avoid delays and handle surges in demand efficiently.
Dive Deep Into the Ethereum Knowledge Base: How Are Gas Fees Calculated?
Gas Limit: The Gas Limit sets the maximum amount of gas a transaction can use. Users can adjust this limit based on the complexity of their transaction. For example, a basic ETH transfer may require a smaller gas limit, while smart contract interactions need higher limits to complete multiple computations. Setting a higher limit ensures that a transaction goes through without running out of gas, though users only pay for the gas consumed.
Gas Price: The Gas Price represents the ETH a user pays per gas unit. This rate fluctuates based on supply and demand within the network. During high network congestion, gas prices rise as more users bid for transaction processing. Conversely, gas prices tend to lower during quieter periods. Gas price and congestion influence transaction speed, as miners prioritize transactions with higher fees.
Calculation Formula: The total Gas Fee for a transaction is calculated by multiplying the Gas Limit by the Gas Price:
Gas Fee = Gas Limit x Gas Price
This formula provides the exact cost in ETH for any transaction, enabling users to estimate fees before confirming them.
Attention: Gas fees can sometimes reach astonishing levels, with reports of users facing fees exceeding $700,000 due to not setting a proper gas limit! This highlights the importance of correctly configuring your gas settings before initiating any transaction. Always ensure you adjust your gas limit based on the complexity of your transaction to avoid such costly mistakes.
Monitor Real-Time Ethereum Gas Prices to Optimize Your Transactions
Understanding the various elements that influence Ethereum gas prices can help users make more informed decisions when transacting:
Network Congestion: When there is heavy traffic on the Ethereum network, gas prices rise. Users must compete for space to process their transactions. This often happens during big events like new token releases. Popular dApps can also cause high network traffic.
Transaction Complexity: Some tasks on Ethereum require more gas than others. Simple ETH transfers use little computing power. However, interacting with dApps or executing smart contracts requires more resources. Higher complexity means users pay more in gas fees.
Smart Contracts vs. Simple Transfers: As mentioned, smart contracts cost more gas than basic ETH transfers. These contracts must verify conditions, execute functions, and store data, all of which require higher gas. This implies multiple steps to complete each task. In contrast, a simple ETH transfer only involves sending tokens from one wallet to another.
Current Rates: Basic ETH transfers cost between $1 and $5 when network traffic is low. The fees rise to about $10 during normal use. During busy times, fees can go above $50. Using apps like DEXs costs even more because they need extra computing power. You can check current gas fees on www.ethereum.org. The Ethereum website shows how network traffic affects transaction prices.
Example of High-Usage Periods: High network traffic can quickly raise gas fees. NFT sales push fees higher as more people make more complex transactions. DeFi activity made fees hit new highs in 2021. Big network updates like "The Merge" also raised fees due to heightened transaction volume. Users paid extra during these times to speed up their transactions. The fees change based on how congested the network is. More users mean higher fees, and the network updates prices based on demand.
But how can you adapt and enjoy lower gas fees yourself? Here are some effective strategies to help you reduce costs:
Timing Transactions: Making transactions during off-peak hours can help users avoid high fees. Activity tends to slow down during early mornings or weekends, reducing congestion and often lowering gas prices.
Using Layer-2 Solutions: Layer-2 solutions like Optimism and Arbitrum help users save on gas costs by processing transactions off the Ethereum mainnet. These networks batch multiple transactions together before sending them to the mainnet, significantly lowering fees.
Choosing Gas Options Wisely: As previously mentioned, users can control fees by setting an appropriate gas limit. While a high gas limit speeds up processing, it may increase costs. Setting a gas limit that matches transaction needs helps users save while ensuring successful processing.
High gas fees on Ethereum have led many users to look for other options. These fees can make it hard to use dApps on the network. Several other blockchain platforms now offer affordable fees and useful features. These options work well for DeFi, NFTs, and smart contracts.
Solana (SOL): Thanks to its unique proof-of-history consensus mechanism, Solana offers extremely fast transaction speeds and low fees. This platform is ideal for decentralized finance (DeFi) projects and NFT marketplaces, providing users with a seamless experience.
Polygon (MATIC): Polygon is a layer-2 scaling solution that enhances Ethereum's capabilities by offering faster and cheaper transactions. It integrates well with Ethereum-based applications, making it a strong alternative for developers looking to reduce costs.
Avalanche (AVAX): Avalanche is known for its high throughput and low latency. It allows users to create and manage their own customized blockchains, all while maintaining low transaction fees, making it suitable for both enterprises and individual developers.
Every Ethereum user should know how gas fees work on the network. These fees play a key role in keeping Ethereum strong and active. They help pay validators who process transactions and maintain the network.
As mentioned, gas fees usually rise when network traffic is high. Yet these costs help Ethereum stay free from central control. The fees support a wide range of dApps and services. Users benefit from a robust ecosystem that encourages innovation and development. Users who grasp both the costs and benefits can make better choices. They can time their transactions accordingly to save money. This knowledge helps build a stronger Ethereum community, leading to better results for everyone who uses the network.
▶️ Watch: What Is GAS? Ethereum High Transaction Fees Explained
Join the Coinmetro community on Discord and Telegram, where forward-thinking traders and investors gather to share insights, explore new opportunities, and dive deep into cryptocurrencies. Should you need any help, please contact our world-class Customer Support Team via 24/7 live chat or email at hello@coinmetro.com.
To become a Coinmetro user today, Sign Up now or head to our new Exchange if you are already registered to experience our premium trading platform.
Etiquetas
Artículos relacionados
Blockchain en la educación: transformando el aprendizaje y la acreditación
¿Qué pasaría si tu expediente académico pudiera verificarse al instante, en cualquier lugar del mundo? Esta es solo una de las preguntas que reflejan…
7m

Cómo comprar Ethereum (ETH) en Coinmetro - paso a paso
¿Quieres comprar Ethereum al instante sin complicaciones? Coinmetro lo hace rápido, sencillo y seguro. Esta guía te muestra los pasos simples para…
3m

Cómo hacer staking de Ethereum (ETH) en Coinmetro de forma rápida, sencilla y segura
¿Quieres ganar ingresos pasivos con tu Ethereum? Con Coinmetro, hacer staking de ETH es un proceso fluido, seguro y fácil para principiantes. En esta…
3m
El papel de la cadena de bloques en la trazabilidad de la cadena de suministro
En 2021, un escándalo sacudió al sector alimentario. Varios proveedores habían etiquetado carne caducada como si fuera fresca. El resultado fue la…
11m